Vanna 简介
Vanna 是一个 MIT 许可的开源 Python RAG(Retrieval-Augmented Generation)框架,可以用来以对话形式与 SQL 数据库交互。
Vanna 提供两种使用方式:
- 代码调用,如
vn.ask("What are the top 10 customers by sales?") - 基于 Flash 的 Web 应用
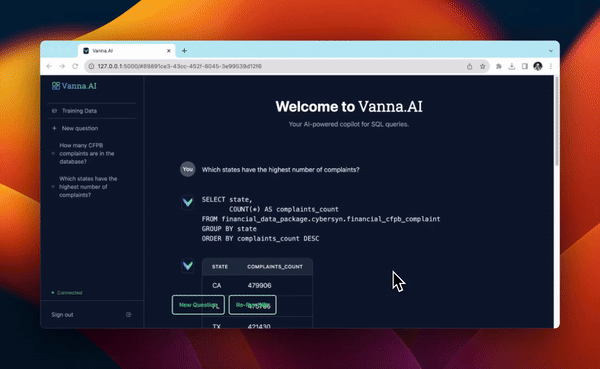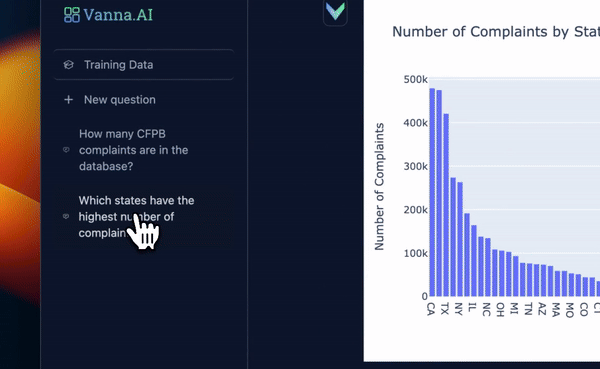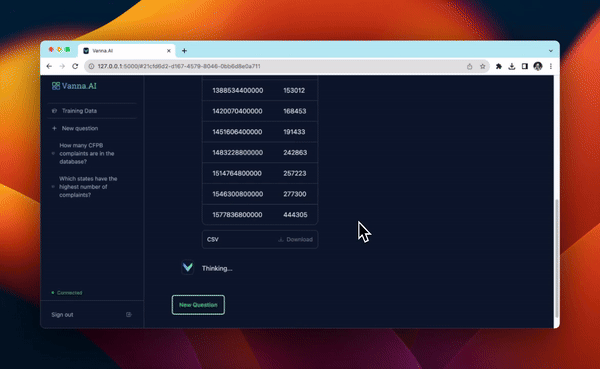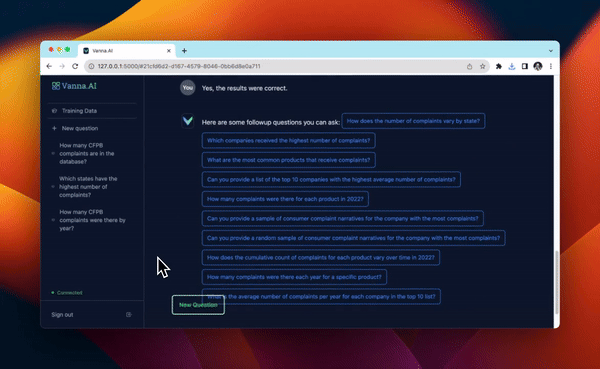
工作原理
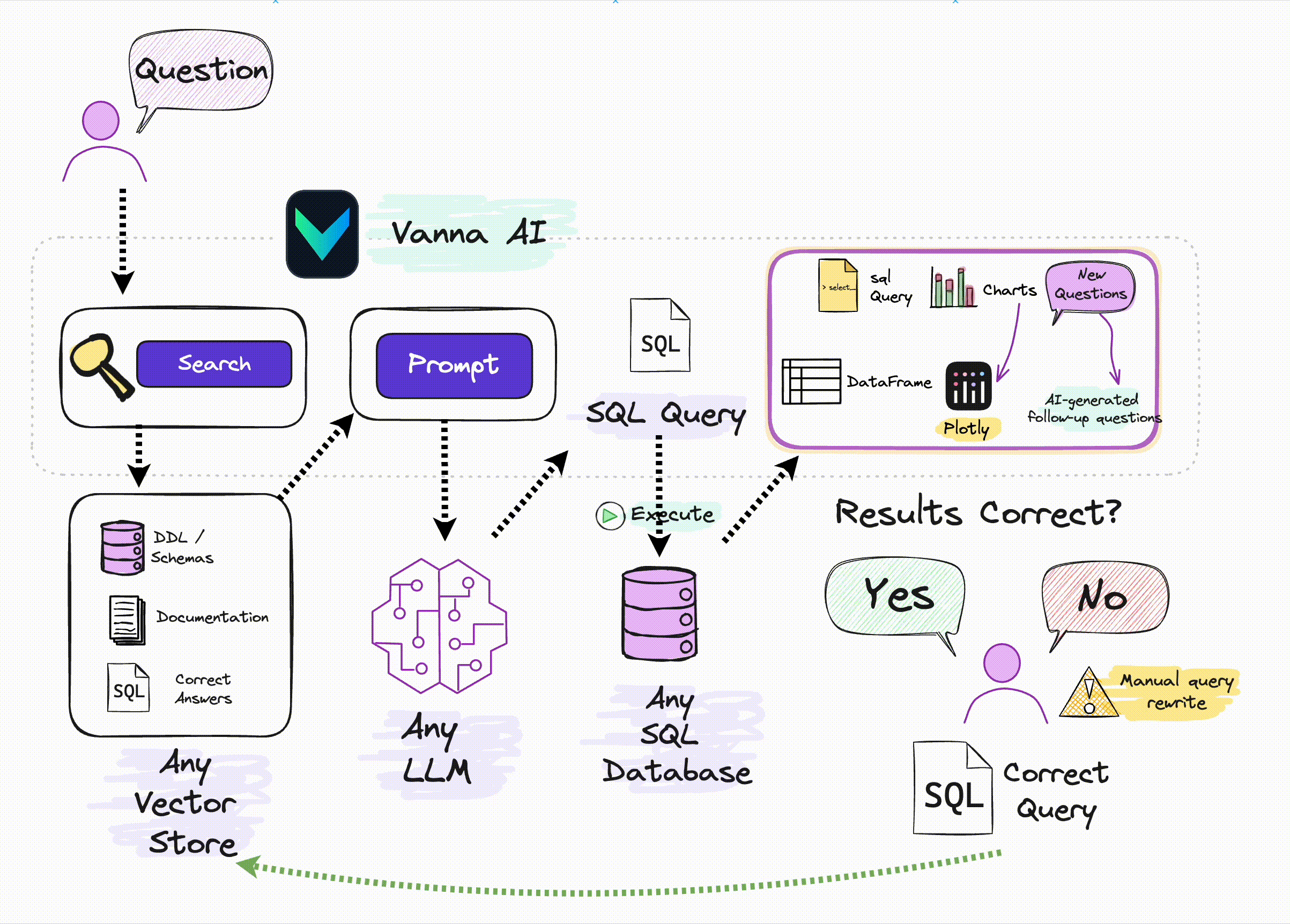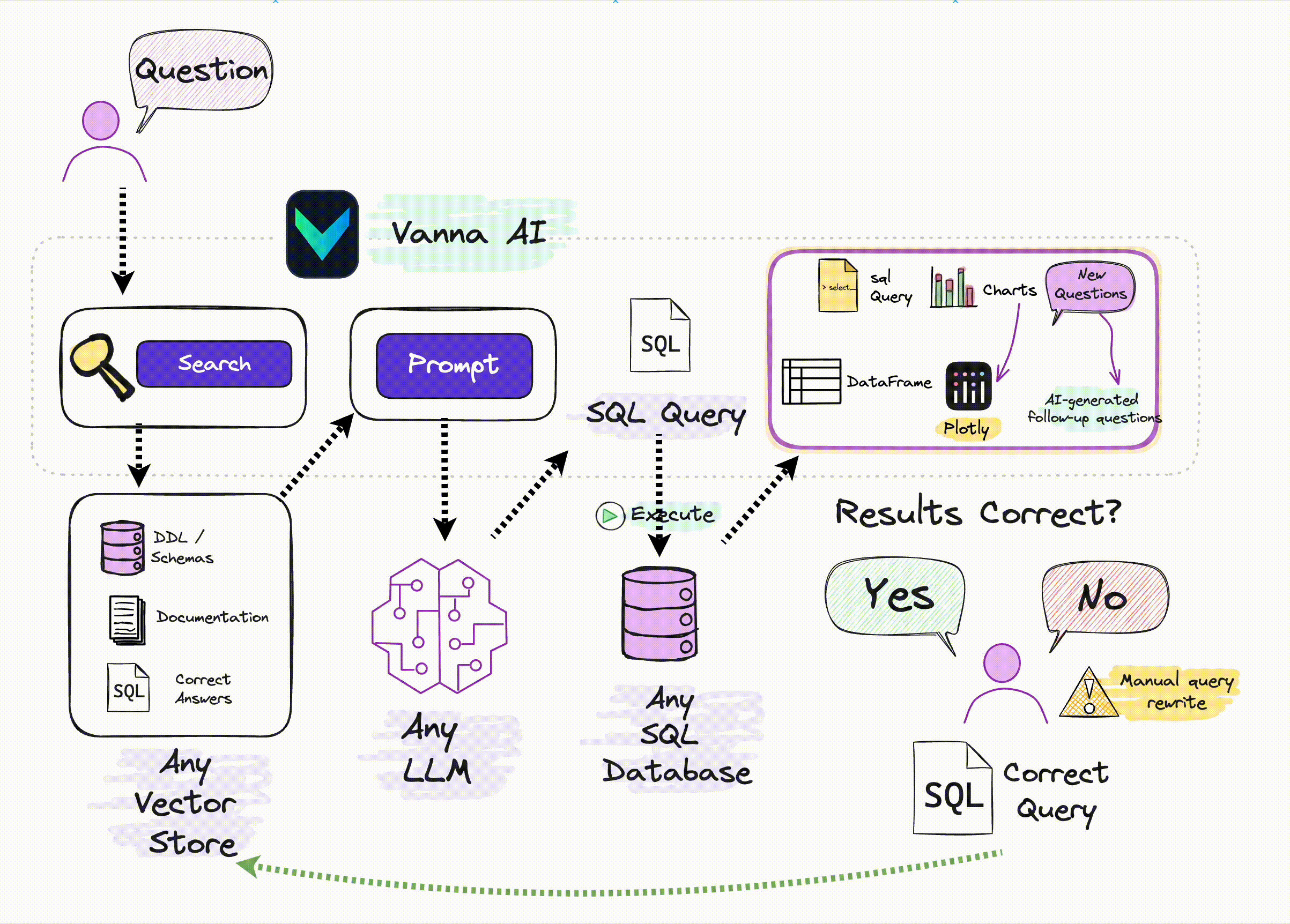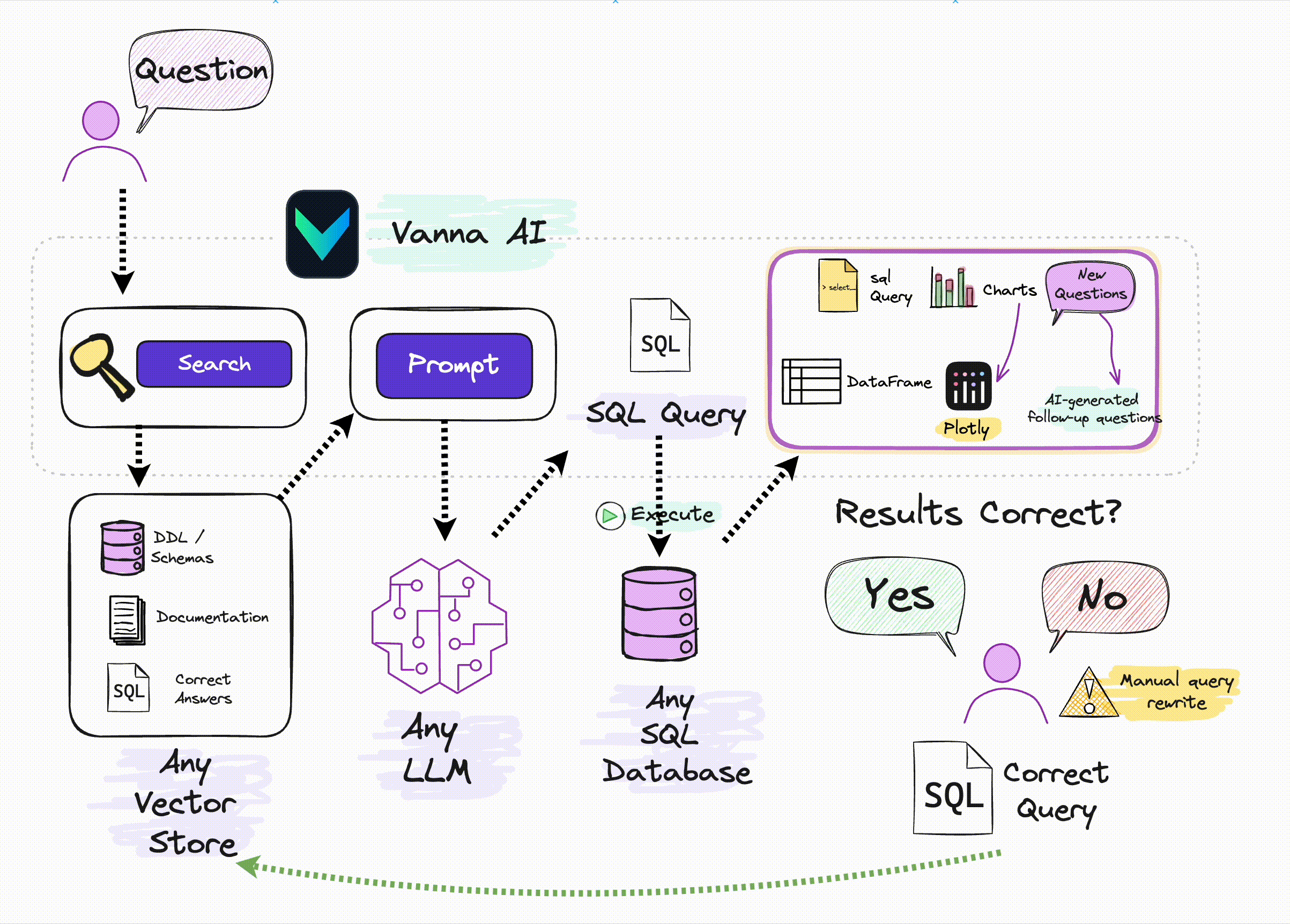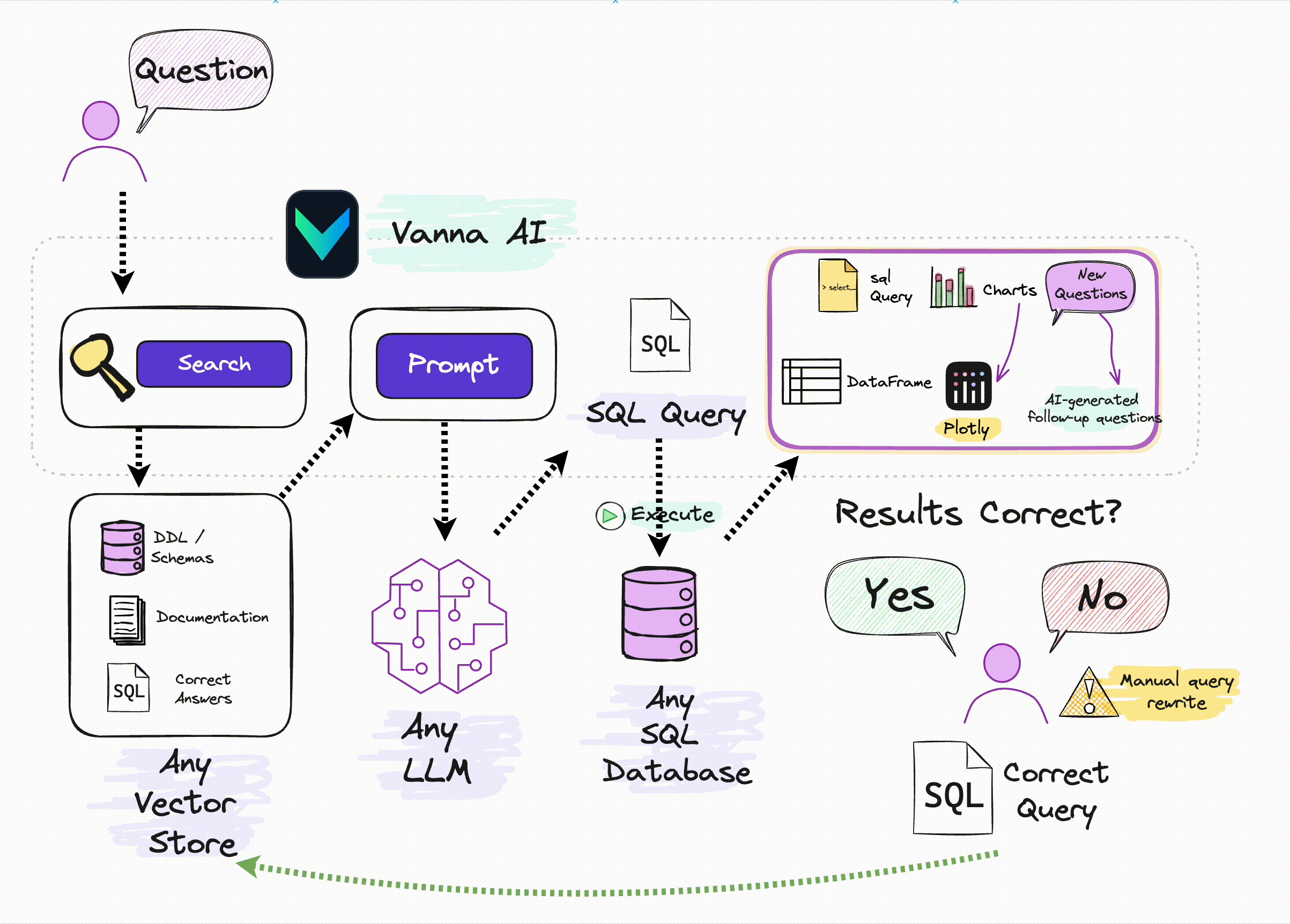
Vanna 的工作原理与通常的 RAG 原理类似,即:
- 先将数据库表的元数据信息、DDL 语句、SQL 查询问答对等信息向量化,存储在向量库中;
- 用户提问时,将问题与向量库中的信息向量进行匹配,找到相关的信息向量,然后将问题和信息向量组织成提示词输入到 LLM 中,生成 SQL 查询语句;
- 用户可对生成的 SQL 进行反馈,正确的 SQL 会被添加到向量库以提高后续问答的精度。
离线环境使用
Quickstart With Sample Data 中提供的示例代码需要从 vanna.ai 获得注册邮箱对应的 api_key:
!pip install vanna
import vanna
from vanna.remote import VannaDefault
vn = VannaDefault(model='chinook', api_key=vanna.get_api_key('my-email@example.com'))
vn.connect_to_sqlite('https://vanna.ai/Chinook.sqlite')
vn.ask("What are the top 10 albums by sales?")离线环境使用时,可以选择构建自定义类型的 Vanna 对象,避免对 vanna.ai 在线环境的依赖。
在 Quickstart With Your Own Data 中,可以根据部署环境选择实际需要使用的 LLM、向量库 和 数据库类型。
以下以 OpenAI + ChromaDB + MySQL 为例进行说明。
Setup
安装依赖(可通过内网源或构建镜像):
$ pip install 'vanna[chromadb,openai,mysql]'准备向量嵌入模型文件,放至 ~/.cache/chroma/onnx_models/all-MiniLM-L6-v2/onnx.tar.gz:
$ wget https://chroma-onnx-models.s3.amazonaws.com/all-MiniLM-L6-v2/onnx.tar.gz也可从 ModelScope all-MiniLM-L6-v2 下载。
构建 Vanna 实例,使用兼容 OpenAI 接口的本地 LLM:
from openai import OpenAI
client = OpenAI(api_key='sk-xxx', base_url='http://127.0.0.1:19131/v1/')
class MyVanna(ChromaDB_VectorStore, OpenAI_Chat):
def __init__(self, config=None):
ChromaDB_VectorStore.__init__(self, config=config)
OpenAI_Chat.__init__(self, client=client, config=config)
vn = MyVanna(config={'model': 'qwen1.5-72b-chat'})配置数据库连接:
vn.connect_to_mysql(host='my-host', dbname='my-db', user='my-user', password='my-password', port=123)“训练”
准备“训练”数据:
# The information schema query may need some tweaking depending on your database. This is a good starting point.
df_information_schema = vn.run_sql("SELECT * FROM INFORMATION_SCHEMA.COLUMNS")
# This will break up the information schema into bite-sized chunks that can be referenced by the LLM
plan = vn.get_training_plan_generic(df_information_schema)
print(plan)执行“训练”:
# If you like the plan, then uncomment this and run it to train
vn.train(plan=plan)这里的“训练”,实际相当于是对数据进行向量化,并添加至向量库,并不涉及对 LLM 的权重调整。
可随时补充“训练”数据:
# The following are methods for adding training data. Make sure you modify the examples to match your database.
# DDL statements are powerful because they specify table names, colume names, types, and potentially relationships
vn.train(ddl='''
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS my-table (
id INT PRIMARY KEY,
name VARCHAR(100),
age INT
)
''')
# Sometimes you may want to add documentation about your business terminology or definitions.
vn.train(documentation="Our business defines OTIF score as the percentage of orders that are delivered on time and in full")
# You can also add SQL queries to your training data. This is useful if you have some queries already laying around. You can just copy and paste those from your editor to begin generating new SQL.
vn.train(sql="SELECT * FROM my-table WHERE name = 'John Doe'")查看“训练数据”:
# At any time you can inspect what training data the package is able to reference
training_data = vn.get_training_data()
print(training_data)或删除“训练数据”:
# You can remove training data if there's obsolete/incorrect information.
vn.remove_training_data(id='1-ddl')对话
对话时,vanna 会从“训练”数据中找出 10 个最相关的信息向量,将其作为输入给 LLM 的提示词的一部分,用以辅助生成 SQL:
vn.ask(question='有哪些表')启动 Web App
from vanna.flask import VannaFlaskApp
VannaFlaskApp(vn, allow_llm_to_see_data=True).run(port=8085, host='0.0.0.0')上面代码会在 8085 端口启动一个 Vanna Flask Web App,更多参数设置可见 Customization。
相关资料
- Can I run this “offline”?
- Vanna Docs: Local
- vanna+qwen实现私有模型的SQL转换
- TEXT2SQL工具vanna本地化安装和应用
- ModelScope all-MiniLM-L6-v2
- Vanna AI:告别代码,用自然语言轻松查询数据库,领先的RAG2SQL技术让结果更智能、更精准!
- how to set allow_llm_to_see_data=True
