自动化测试相关概念
测试用例
测试用例是一组输入、执行条件和预期结果的集合,用于验证软件系统的正确性。
自动化测试
自动化测试是指使用自动化工具或脚本来执行测试用例,以减少人工测试的工作量,提高测试效率和准确性。
测试金字塔
测试金字塔 是一种指导自动化测试策略的框架,它建议在不同层次上分配不同数量和类型的测试,以确保成本效益、减轻团队负担并提高测试准确性。这个概念最初由 Mike Cohn 提出,主要分为三个层次:单元测试(Unit Tests)、服务测试(Service Tests,也称为集成测试)、以及用户界面测试(UI Tests)。越靠近塔底的测试类型执行的速度越快、越稳定(不易发生变化);越靠近塔尖的测试类型编写成本越高、收益越低。
人们对测试金字塔中测试的类型有不同的划分,但是总体的思想是一致的。
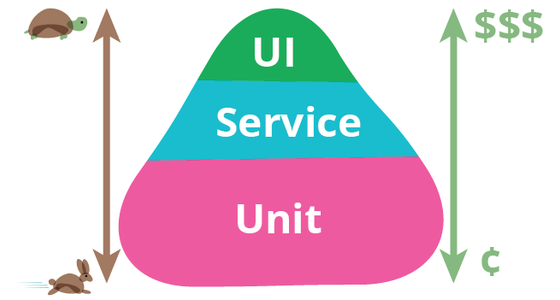
单元测试
单元测试是金字塔的基础层,它们不依赖外部资源(如数据库、网络等)快速、独立,并且数量众多,专注于单个代码单元的行为验证。
集成测试
集成测试位于中间层,测试不同组件之间的交互,数量相对较少。
用户界面测试
UI测试或端到端测试位于金字塔的顶层,覆盖从用户角度的完整交互流程,但数量最少,因为它们成本高且维护难度大。
Mocking & Stubbing
Mocking(模拟)是指创建一个模拟对象来代替实际的依赖对象。这个模拟对象会按照测试的需要来行为,通常用于验证被测试代码是否按照预期与依赖项交互。
Stubbing(存根)与 Mocking 类似,但更侧重于提供预定义的返回值或行为,而不是验证交互。Stub 对象用于替换实际的依赖对象,以便在测试中控制或预测它们的输出。
在实际的软件开发中,Mocking 和 Stubbing 通常结合使用,以创建一个可控的测试环境。
区别
- 目的:Mocking 主要用于验证代码与依赖项的交互,而 Stubbing 主要用于控制测试环境,提供可预测的输出。
- 行为:Mock 可以在测试中模拟更复杂的行为,如条件返回或引发异常,而 Stub 通常只提供简单的固定返回值。
- 验证:Mock 对象可以在测试后验证方法是否被正确调用,包括调用次数和参数,而 Stub 通常不进行这种验证。
测试覆盖率
测试覆盖率,反映了测试用例对软件代码的覆盖程度,通常以百分比来表示。
测试覆盖率是一种度量标准,用于衡量测试是否覆盖了代码的各个部分,例如语句覆盖、分支覆盖、条件覆盖、路径覆盖等。
测试覆盖率越高,意味着测试用例覆盖的代码越多,但并不意味着测试用例的质量越高,100% 的测试覆盖率也不能保证软件完全没有缺陷,所以在设计测试用例时,应该注重测试用例的质量。
测试驱动开发
测试驱动开发(Test-Driven Development,简称TDD)是一种软件开发流程,其核心理念是先编写测试用例,再编写能够通过这些测试用例的代码。TDD的目的是确保代码的可测试性、可维护性和质量。
自动化测试常用工具
Build Tool
通常情况下,构建工具(如 Maven、Gradle)会在项目构建过程中自动执行测试用例。
以 Maven 为例,可在 https://start.spring.io/ 生成一个 Spring Boot 项目,解压后可以找到一个 src/test/java/com/example/demo/DemoApplicationTests.java 测试类:
package com.example.demo;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
@SpringBootTest
class DemoApplicationTests {
@Test
void contextLoads() {
}
}使用 Maven 运行测试用例:
$ mvn test
...
[INFO] -------------------------------------------------------
[INFO] T E S T S
[INFO] -------------------------------------------------------
[INFO] Running com.example.demo.DemoApplicationTests
...
[INFO] Tests run: 1, Failures: 0, Errors: 0, Skipped: 0, Time elapsed: 1.843 s -- in com.example.demo.DemoApplicationTests
[INFO]
[INFO] Results:
[INFO]
[INFO] Tests run: 1, Failures: 0, Errors: 0, Skipped: 0
[INFO]
[INFO] ------------------------------------------------------------------------
[INFO] BUILD SUCCESS
[INFO] ------------------------------------------------------------------------
...执行 mvn package 命令时也会自动执行测试用例,如果测试用例失败,构建过程会终止。如果需要跳过测试用例,可以使用 -DskipTests 参数:
mvn package -DskipTestsJUnit
JUnit 是一个 Java 编程语言的单元测试框架,用于编写和运行重复测试。JUnit 提供了注解和断言来编写测试用例,可以方便地进行测试驱动开发。
当前 Junit 的主要版本是 JUnit 5,上一个主要版本 JUnit 4 的最后发布版 4.13.2 是 2021 年发布的。
JUnit5
不同于之前版本的 JUnit,JUnit 5 是由三个不同的子项目组成的模块化测试框架:
JUnit 5 = JUnit Platform + JUnit Jupiter + JUnit Vintage
JUnit Platform负责在 JVM 中启动测试框架。它定义了 TestEngine API 用来开发可在其平台上运行的测试框架。JUnit Jupiter包含了对 JUnit 5 新注解的支持,并提供了一个能够运行 JUnit 5 测试用例的TestEngine实现。JUnit Vintage提供了用于运行 JUnit 3 和 JUnit 4 的测试用例的TestEngine实现。
| JUnit 5 常用注解 | 作用 | JUnit 4 对应注解 |
|---|---|---|
@Test |
标记一个方法是测试方法 | @Test |
@BeforeEach |
在每个测试方法之前都执行的方法 | @Before |
@AfterEach |
在每个测试方法之后都执行的方法 | @After |
@BeforeAll |
在所有测试方法之前执行一次的方法,需要 static |
@BeforeClass |
@AfterAll |
在所有测试方法之后执行一次的方法,需要 static |
@AfterClass |
@Disabled |
禁用测试类或方法 | @Ignore |
更多注解可见 2.1. Annotations 。
JUnit5 基础注解
package com.example.demo;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.*;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
@SpringBootTest
class DemoApplicationTests {
private static Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(DemoApplicationTests.class);
@BeforeAll
static void setup() {
LOGGER.info("@BeforeAll - executes once before all test methods in this class");
}
@BeforeEach
void init() {
LOGGER.info("@BeforeEach - executes before each test method in this class");
}
@AfterEach
void tearDown() {
LOGGER.info("@AfterEach - executed after each test method.");
}
@AfterAll
static void done() {
LOGGER.info("@AfterAll - executed after all test methods.");
}
@Test
void contextLoads() {
}
@DisplayName("Single test successful")
@Test
void testSingleSuccessTest() {
LOGGER.info("Success");
}
@Test
@Disabled("Not implemented yet")
void testShowSomething() {
}
}$ mvn test
...
17:34:33.848 [main] INFO com.example.demo.DemoApplicationTests -- @BeforeAll - executes once before all test methods in this class
. ____ _ __ _ _
/\\ / ___'_ __ _ _(_)_ __ __ _ \ \ \ \
( ( )\___ | '_ | '_| | '_ \/ _` | \ \ \ \
\\/ ___)| |_)| | | | | || (_| | ) ) ) )
' |____| .__|_| |_|_| |_\__, | / / / /
=========|_|==============|___/=/_/_/_/
:: Spring Boot :: (v3.3.2)
2024-08-08T17:34:34.251+08:00 INFO 35736 --- [demo] [ main] com.example.demo.DemoApplicationTests : Starting DemoApplicationTests using Java 17.0.2 with PID 35736 (started by alphahinex in /Users/alphahinex/Desktop/demo)
2024-08-08T17:34:34.253+08:00 INFO 35736 --- [demo] [ main] com.example.demo.DemoApplicationTests : No active profile set, falling back to 1 default profile: "default"
2024-08-08T17:34:34.957+08:00 INFO 35736 --- [demo] [ main] com.example.demo.DemoApplicationTests : Started DemoApplicationTests in 1.063 seconds (process running for 2.405)
OpenJDK 64-Bit Server VM warning: Sharing is only supported for boot loader classes because bootstrap classpath has been appended
2024-08-08T17:34:35.904+08:00 INFO 35736 --- [demo] [ main] com.example.demo.DemoApplicationTests : @BeforeEach - executes before each test method in this class
2024-08-08T17:34:35.911+08:00 INFO 35736 --- [demo] [ main] com.example.demo.DemoApplicationTests : @AfterEach - executed after each test method.
2024-08-08T17:34:35.933+08:00 INFO 35736 --- [demo] [ main] com.example.demo.DemoApplicationTests : @BeforeEach - executes before each test method in this class
2024-08-08T17:34:35.934+08:00 INFO 35736 --- [demo] [ main] com.example.demo.DemoApplicationTests : Success
2024-08-08T17:34:35.935+08:00 INFO 35736 --- [demo] [ main] com.example.demo.DemoApplicationTests : @AfterEach - executed after each test method.
2024-08-08T17:34:35.940+08:00 INFO 35736 --- [demo] [ main] com.example.demo.DemoApplicationTests : @AfterAll - executed after all test methods.
[WARNING] Tests run: 3, Failures: 0, Errors: 0, Skipped: 1, Time elapsed: 2.521 s -- in com.example.demo.DemoApplicationTests
[INFO]
[INFO] Results:
[INFO]
[WARNING] Tests run: 3, Failures: 0, Errors: 0, Skipped: 1
...从输出的日志信息可以看到,@BeforeAll 和 @AfterAll 的日志只打印了一次,@BeforeEach 和 @AfterEach 的日志在每个没 @Disabled 的 @Test 方法执行前后都会打印。
JUnit5 断言
断言是测试用例最重要的组成部分。
断言可以用来验证方法的行为是否符合预期,并在断言失败时使测试用例失败,进而体现到最终的测试报告中。
可以说没有断言的测试用例没有任何意义,因为测试用例始终会执行通过。
JUnit 5 的断言都包含在 org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions 类的静态方法中,并支持了 Lambda 表达式等 Java 新特性,常见的断言包括:
assertTrue:用于验证条件是否为true。assertFalse:用于验证条件是否为false。assertNull:用于验证对象是否为null。assertNotNull:用于验证对象是否不为null。assertEquals:用于验证两个对象是否相等。assertNotEquals:用于验证两个对象是否不相等。assertArrayEquals:用于验证两个数组是否相等。assertSame:用于验证两个对象是否是同一个对象。assertNotSame:用于验证两个对象是否不是同一个对象。assertThrows:用于验证方法是否抛出了指定的异常。assertAll:用于组合多个断言,当其中一个断言失败时,后续断言不会执行。
@Test
void groupAssertions() {
int[] numbers = {0, 1, 2, 3, 4};
assertNotNull(numbers);
assertAll("numbers",
() -> assertEquals(0, numbers[0]),
() -> assertSame(3, numbers[3]),
() -> assertArrayEquals(new int[]{0, 1, 2, 3, 4}, numbers)
);
}JUnit5 假设
假设用来在测试方法中定义前提条件,如果假设不成立,则测试方法会被忽略。
JUnit 5 的假设方法包含在 org.junit.jupiter.api.Assumptions 类中,有三类静态方法:
assumeTrue:假设条件为true,否则忽略测试方法。assumeFalse:假设条件为false,否则忽略测试方法。assumingThat:假设条件为true,否则忽略测试方法。
@Test
void testOnlyOnCiServer() {
assumeTrue("CI".equals(System.getenv("ENV")));
// remainder of test
}JUnit5 验证异常
JUnit 5 中不再使用之前的 @Test(expected = …) 和 ExpectedException 规则来设定期待抛出的异常。异常的验证都通过 Assertions.assertThrows(…) 方法实现:
@Test
void shouldThrowException() {
Throwable exception = assertThrows(UnsupportedOperationException.class, () -> {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("Not supported");
});
assertEquals("Not supported", exception.getMessage());
}
@Test
void assertThrowsException() {
String str = null;
assertThrows(IllegalArgumentException.class, () -> {
Integer.valueOf(str);
});
}DbUnit
DbUnit 是一个 JUnit 4 的扩展,可以在测试过程中基于 XML 数据集管控测试数据库中数据状态,最后的发布版本是 2024年06月02日 的 v2.8.0。
基本思路是继承 DBTestCase 基类后,通过实现 getDataSet() 方法,将准备的 XML 格式数据文件加载到测试库中,之后通过 org.dbunit.Assertion 中的断言进行数据验证。
如果想在 JUnit 5 中使用 DbUnit,需要在依赖中添加 JUnit 4 和 JUnit Vintage 引擎:
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.junit.vintage</groupId>
<artifactId>junit-vintage-engine</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>以下是一个使用 DbUnit 的示例:
com.example.demo.DataSourceDBUnitTest:
package com.example.demo;
import org.dbunit.Assertion;
import org.dbunit.DataSourceBasedDBTestCase;
import org.dbunit.dataset.IDataSet;
import org.dbunit.dataset.ITable;
import org.dbunit.dataset.xml.FlatXmlDataSetBuilder;
import org.dbunit.operation.DatabaseOperation;
import org.h2.jdbcx.JdbcDataSource;
import org.junit.Test;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
public class DataSourceDBUnitTest extends DataSourceBasedDBTestCase {
@Override
protected DataSource getDataSource() {
JdbcDataSource dataSource = new JdbcDataSource();
dataSource.setURL(
"jdbc:h2:mem:default;MODE=LEGACY;DB_CLOSE_DELAY=-1;init=runscript from 'classpath:dbunit/schema.sql'");
dataSource.setUser("sa");
dataSource.setPassword("sa");
return dataSource;
}
@Override
protected IDataSet getDataSet() throws Exception {
return new FlatXmlDataSetBuilder().build(getClass().getClassLoader()
.getResourceAsStream("dbunit/data.xml"));
}
@Override
protected DatabaseOperation getSetUpOperation() {
return DatabaseOperation.REFRESH;
}
@Override
protected DatabaseOperation getTearDownOperation() {
return DatabaseOperation.DELETE_ALL;
}
@Test
public void testGivenDataSetEmptySchema_whenDataSetCreated_thenTablesAreEqual() throws Exception {
IDataSet expectedDataSet = getDataSet();
ITable expectedTable = expectedDataSet.getTable("CLIENTS");
IDataSet databaseDataSet = getConnection().createDataSet();
ITable actualTable = databaseDataSet.getTable("CLIENTS");
Assertion.assertEquals(expectedTable, actualTable);
}
}src/test/resources/dbunit/schema.sql:
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS CLIENTS
(
`id` int AUTO_INCREMENT NOT NULL,
`first_name` varchar(100) NOT NULL,
`last_name` varchar(100) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
);
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS ITEMS
(
`id` int AUTO_INCREMENT NOT NULL,
`title` varchar(100) NOT NULL,
`produced` date,
`price` float,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
);src/test/resources/dbunit/data.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<dataset>
<CLIENTS id='1' first_name='Charles' last_name='Xavier'/>
<ITEMS id='1' title='Grey T-Shirt' price='17.99' produced='2019-03-20'/>
<ITEMS id='2' title='Fitted Hat' price='29.99' produced='2019-03-21'/>
<ITEMS id='3' title='Backpack' price='54.99' produced='2019-03-22'/>
<ITEMS id='4' title='Earrings' price='14.99' produced='2019-03-23'/>
<ITEMS id='5' title='Socks' price='9.99'/>
</dataset>更多 DbUnit 用法可参见 Introduction to DBUnit 及 Getting Started 等文档。
个人感觉 Spring Framework 下的 Spring TestContext Framework 中所提供的 Executing SQL Scripts 方式面向 SQL,相比 XML 更加直观,且无需引入三方依赖,对 JUnit 版本也没有限制。
Mockito
Mockito 是 Java 生态常用的 Mock 框架,用于创建和配置 Mock 对象,以及验证测试中的行为。Mockito 会被 Spring Boot Starter 自动依赖,无需额外引入。
org.mockito.Mockito 类中常用的静态方法包括:
mock:创建一个 Mock 对象。verify:验证 Mock 对象的行为。spy:创建一个部分 Mock 的对象,真实方法会被调用,但依然可以进行验证和 stub。when:配置 Mock 对象的行为。
@Test
void mockAndVerify() {
List<String> mockedList = mock(List.class);
mockedList.add("one");
mockedList.add("two");
mockedList.add("two");
mockedList.add("three");
verify(mockedList).add("three");
verify(mockedList, times(2)).add("two");
verify(mockedList, atLeastOnce()).add("three");
verify(mockedList, atMost(3)).add("one");
}
@Test
void spyAndStub() {
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
List<String> spiedList = spy(list);
spiedList.add("one");
spiedList.add("two");
spiedList.add("three");
assertEquals(3, spiedList.size());
when(spiedList.get(0)).thenReturn("first");
assertEquals("first", spiedList.get(0));
assertEquals("two", spiedList.get(1));
}JaCoCo
JaCoCo 是 Java 的代码覆盖率工具,可与 Maven 或 Gradle 集成,用于生成代码覆盖率报告。
在 Maven 中使用 JaCoCo 插件,只需在 pom.xml 中添加以下配置:
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.jacoco</groupId>
<artifactId>jacoco-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>0.8.12</version>
<executions>
<execution>
<goals>
<goal>prepare-agent</goal>
</goals>
</execution>
<execution>
<id>report</id>
<phase>test</phase>
<goals>
<goal>report</goal>
</goals>
</execution>
</executions>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>执行 mvn test 后,JaCoCo 会生成一个 target/site/jacoco/index.html 的代码覆盖率报告。
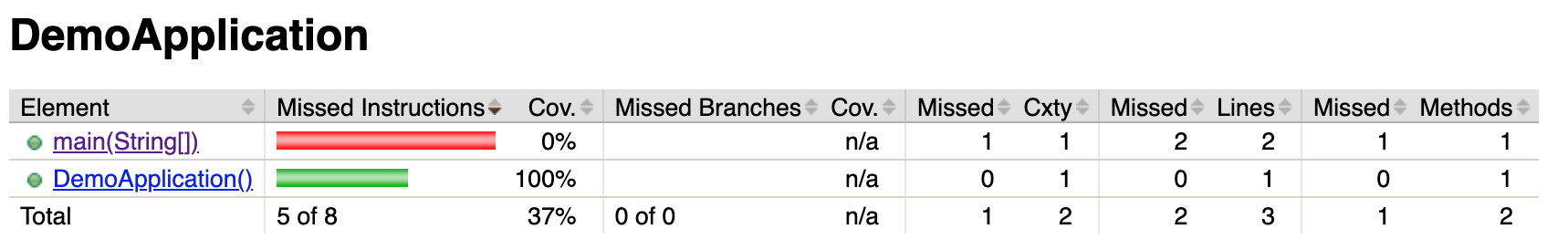
示例代码
完整示例代码可见:https://github.com/AlphaHinex/java-test-demo
相关资料
- A Guide to JUnit 5
- 微服务的自动化集成测试实战
- 写测试用例都这么简单了,你不来试试?
- 使用 Postman 进行系统可接受性测试
- 借助 Data File 实现请求数据与 Postman 脚本的分离
- ApacheBench 简介
- 构造 ApacheBench 可用的 postfile
- Sonar Quality Gates
